Understanding Marketing Attribution Models to pick the right approach
Let’s start with a question: How many channels do you use in your marketing today? According to Invespcro 73% of marketers leverage a multichannel targeting approach.
This means, that almost three-quarter of us use more than one channel to communicate with our prospects, leads, and customers.
But how do we know what’s working and what’s not? In fact, 77% of marketers are unsure if they use the right attribution model.
What is marketing attribution?
Marketing attribution assigns credit to marketing touchpoints and conversion steps across the customer journey and sales funnel. That way, we can attribute revenue to marketing initiatives. For example, if a lead converts through a Google Ad campaign and becomes a customer, we can give credit to the very campaign, ad group, and even keyword.
Marketing attribution helps marketers to analyze their campaigns and spending to optimize the customer journey, ultimately generating and influencing more revenue for the business.
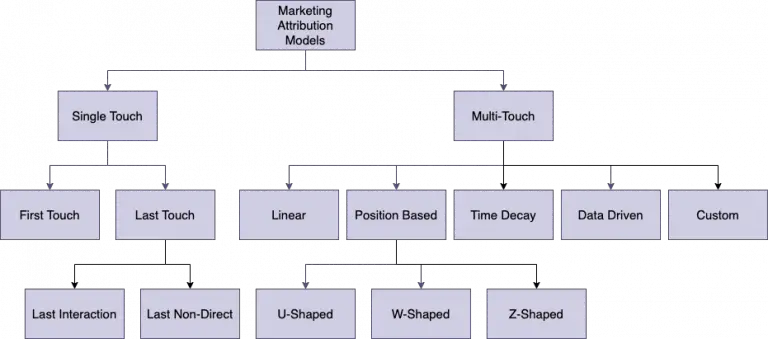
There are different attribution types and models to choose from: single touch vs multi-touch marketing attribution. Each type has different models like first or last click (single touch), or linear, position-based, or data-driven attribution (multi-touch).
Why is marketing attribution important? (Benefits)
Marketing attribution is important for marketers to plan and optimize their efforts. At the end of the day, we want to maximize the outcomes for the available resources. We’ve compiled 5 benefits of marketing attribution:
1. Optimized marketing spend
If we have a budget of $10,000 per month, we need to know how to allocate the budget most effectively. Marketing attribution helps to see the bottom line impact of each channel. Therefore, we can shift budgets to better-performing campaigns and reduce spend on (relative) underperforming initiatives.
2. Personalization
When we know when and how leads interact with our marketing, we can improve personalization at each stage of the sales funnel. We can optimize creatives or entire communications steps.
3. Optimizing the user journey
If we know that certain campaigns convert better than others, we can deliver related information at the right time to increase the value we bring to our leads.
4. Increase ROI
Spending more effectively, as well as communicating more personalized and relevant, will increase the overall campaign performance by reducing the costs per action and simultaneously increasing attributed revenue.
ROI is impacted by the investment but also the outcome, if we optimize both the ROI will increase exponentially.
5. Product development
Product development might not be directly related to marketing attribution, but understanding the pain points of our target audience can guide product roadmaps to deliver a better solution.
Challenges with marketing attribution
Marketing attribution comes with its challenges. For example, 59% of marketers say that creating a culture of measurement and accuracy is the biggest attribution challenge they are facing.
- Offline events and conversions
- Data privacy regulations make it more difficult to measure online events
- Unify all marketing channels in one place
- Picking the right attribution model
- Implementing attribution models
- Accountability and ownership within the organization to maintain data quality
- Taking insights from the attribution reporting and turning it into actions
- Cost for sophisticated attribution software
How to measure marketing attribution
In order to implement marketing attribution, marketers need to use attribution models. The first step is to define and align to the right attribution model for your business and then implement the model correctly. You can have multiple attribution models and create different reports.
What are marketing attribution models?
Marketing attribution models are generally person-based models. That means, that the attribution and user journey of a single person is measured. Of course, this methodology can be applied to companies and user groups, but in most cases, it’s a person-by-person technique.
Attribution models assign credit to marketing tactics based on interaction with a person. This could be lead capturing, opportunity creation, or the last touch before winning a new customer.
Different marketing attribution models use different methodologies when and how much credit to give for each touchpoint.
The goal of attribution models is to measure the marketing touchpoints in a quantitative and qualitative way, in order to further optimize marketing campaigns.
Different types of attribution modeling
There are different types of marketing attribution categories that each has different models. Each category and ultimately model comes with unique benefits, but also challenges.
Touchpoint | A | B | C | D | E |
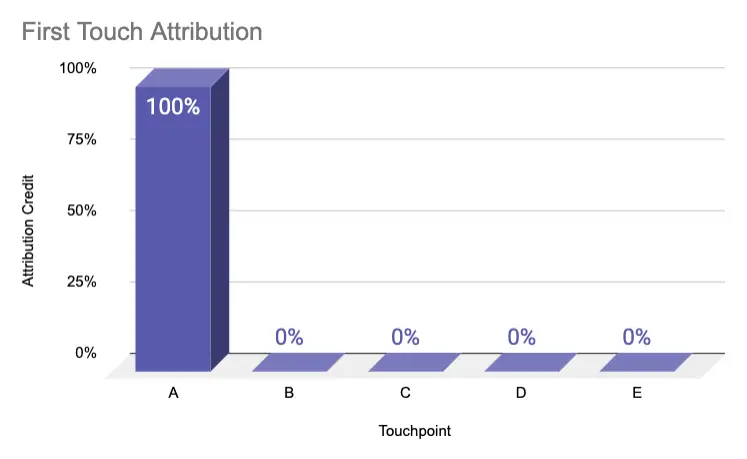
First Touch | 100% | 0% | 0% | 0% | 0% |
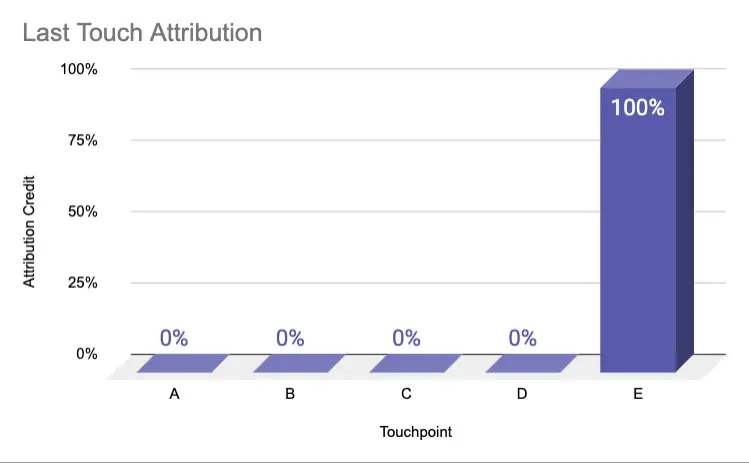
Last Touch | 0% | 0% | 0% | 0% | 100% |
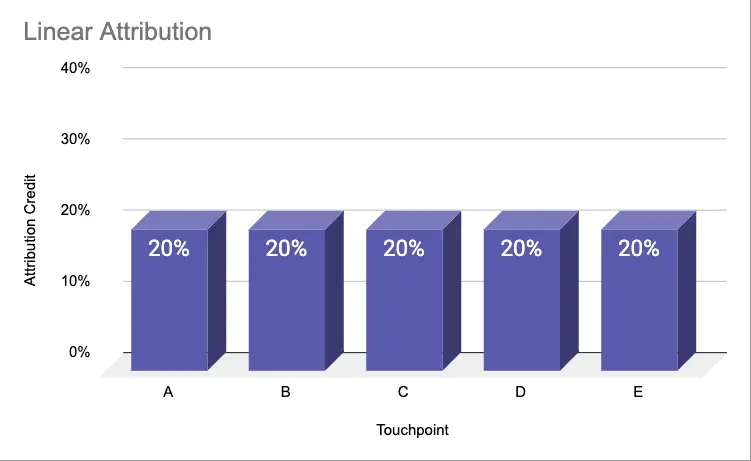
Linear | 20% | 20% | 20% | 20% | 20% |
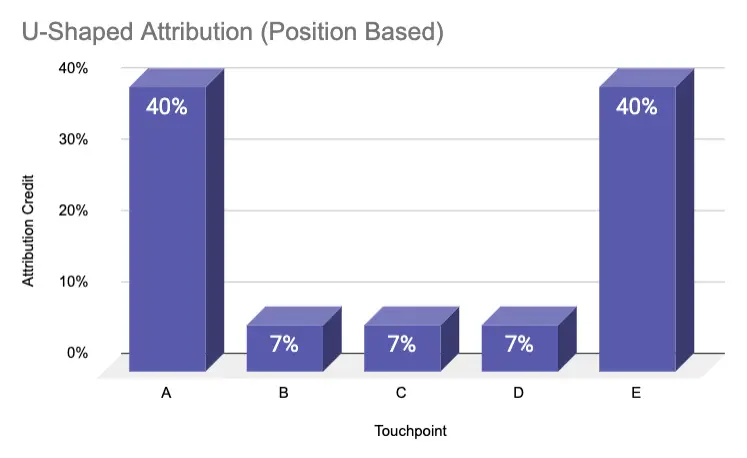
U-Shaped | 40% | 6.7% | 6.7% | 6.7% | 40% |
W-Shaped | 30% | 5% | 30% | 5% | 30% |
Time Decay | 5% | 10% | 15% | 30% | 40% |
Data-Driven | 15% | 5% | 25% | 20% | 35% |
Single touch vs multi-touch attribution
Single touch attribution gives the credit for the attribution to a single touchpoint in the user journey. This is usually the first or last touchpoint. In contrast, multi-touch attribution models allocate the attribution across multiple events.
Both models have advantages and disadvantages and different use cases.
Single touch attribution models
Single touch attribution models give 100% of the credit to one touchpoint in the user journey. This is either the first touch or last touch, whereas the last touch can be distinguished in two different methods: Last interaction or last non-direct click. In Google Analytics, for example, marketers can apply the last non-direct click attribution to give credit to the last interaction that was not from the direct traffic source.
Single touch attribution models are used to identify channels that either convert net new leads or are the last interaction before generating revenue. Usually, this approach is used for transactional companies like e-commerce.
Furthermore, it can be distinguished between a click attribution model and non-click attribution. For example, if a paid search campaign was seen but not clicked, and a Facebook Ad was clicked instead. The click would get the credit in a click-based attribution.
Multi-touch attribution models
Multi-touch attribution (MTA) allocated the credit along the entire buying journey. Each MTA model divvies the credit across the user path differently.
Multi-touch attribution is used when it’s hard to pinpoint a single interaction as the true revenue source. It also reflects the user journey more realistically.
Linear attribution model
The revenue gets attributed equally across all touchpoints. That means that each marketing interaction receives equal credit regardless of when it occurred in the sales journey.
Position based attribution
Depending on the position of the touchpoint in the conversion funnel, the attribution varies based on the applied model.
Position based attribution models are usually referenced by letters that describe the form of the attribution path.
U-shaped attribution
The U-shaped attribution model gives the most credit to the first and last touch with 40% each and allocated the remaining 20% across the interactions in between.
W-shaped attribution
The W-shaped model attributes the majority of revenue credit to the first, last, and most important middle touchpoint. The middle touchpoint is usually when the lead becomes a qualified lead. For example, requesting a sales demo.
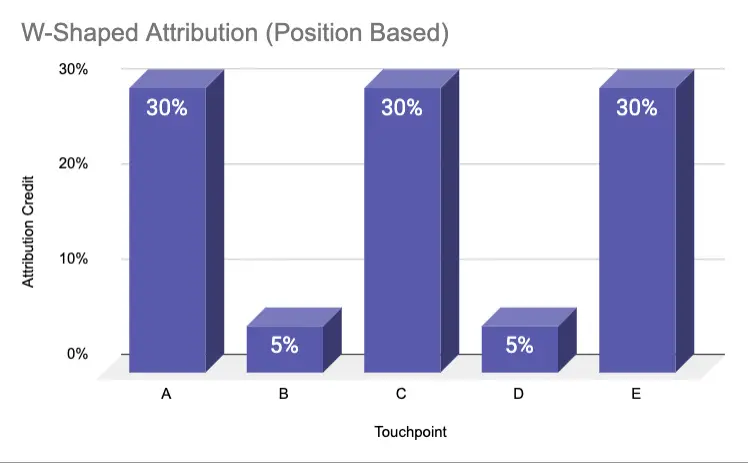
Each of the 3 major touch-points receives 30% credit, whereas the remaining customer interactions receive 5%.
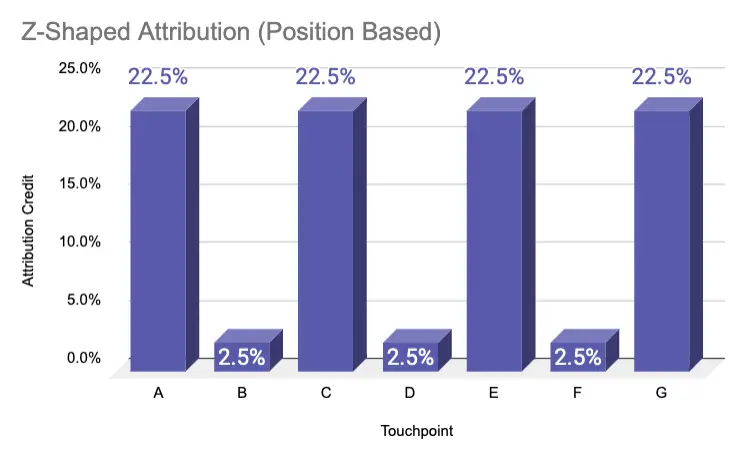
Z-shaped attribution
In the Z-shaped multi-touch attribution model, multiple touchpoints across the buying journey receive partial credit. It’s expanding on the W-shaped model by giving the majority of the credit to the four most important interactions, with 22.5% each. The remaining touchpoints in between the major revenue drivers receive 2.5%. This model only works with at least 7 user interactions.
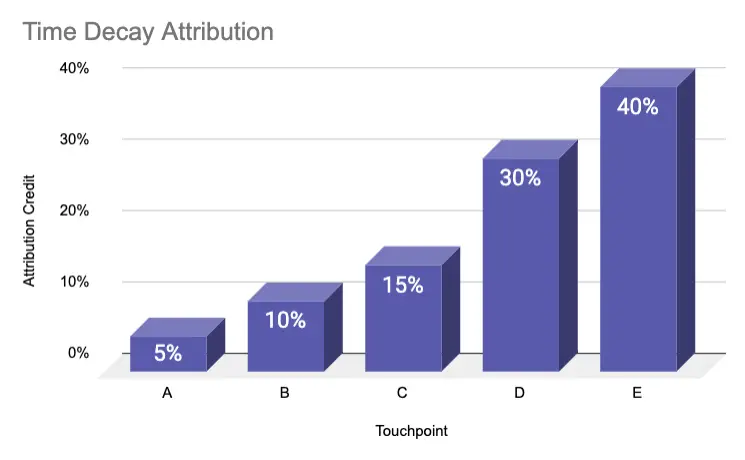
Time decay attribution model
The time decay marketing attribution follows the logic that each touchpoint close to the purchase gets more credit than the previous interaction. Over time, the revenue impact decays.
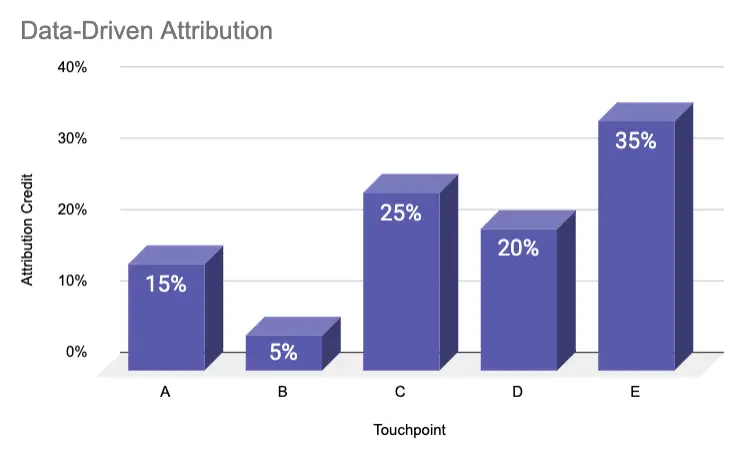
Data-driven and custom attribution model
Data-driven attribution uses data points based on how people engage with your marketing efforts and applies algorithms and machine learning to give credit to individual touchpoints. Data-driven attribution is gaining popularity in advertising tools such as Google Ads. Google analyzes the user journey of how they engage with your ads (number of clicks, times in between actions, etc.) and attributes conversions accordingly.
Alternatively, it’s common to use a custom attribution model to define specific actions or key milestones in the buying journey.
Marketing attribution software and tools
One-third of marketers believe that having the right technologies to collect and analyze data has the biggest impact on understanding their customers. Moreover, HubSpot says that a little more than 50 % are currently using attribution reporting.
In essence, marketing attribution software and tools can not just help with revenue attribution and uncovering the customer journey, they are mandatory. We all have access to free tools like Google Analytics, but using it correctly and interpreting the data is a big challenge.
Many marketers (42%) still use manual spreadsheets for marketing attribution tracking and reporting.
Action: Check the capabilities of your existing martech stack. For example, you might be using HubSpot as a CRM and don’t leverage the attribution reporting yet, or haven’t set up Google Analytics in the best possible way.
When your current technology reaches limitations – like for ABM reporting – it’s time to turn to more robust tools like Bizable, DreamData.io, or LeadsRx.
When to choose which model?
Unfortunately, it really depends which marketing attribution model is the right one for you on multiple factors. Some of which are:
- Are you a B2B or B2C business?
- How many touchpoints does your sales cycle usually have?
- Do you have the technology to support attribution reporting?
- What data do you want to uncover? For example, first touch attribution can be powerful to uncover the value of a new net lead generation advertising campaign.
Generally speaking, the more transactional and fewer marketing interactions you have, the easier your attribution reporting can be.
I just want to finish with this: You don’t have to choose one single attribution model. You should implement multiple and look at each reporting individually and take insights. Lastly, it’s more important to use the insights and take action than collecting all this data and don’t act on it.

Sascha is a Lifecycle Marketing Consultant with over 8 years of digital marketing experiences in Silicon Valley, the UK, and Germany.
After leading the demand generation for a 100+ million company, he decided to venture out on himself. He’s now helping clients to attract and convert more leads and customers.
His main focus are SEO, paid media & marketing automation – all with the focus to tie marketing campaigns to revenue.
Sascha has been featured in industry publications.